Difference between revisions of "ERROR BARS"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "<div style="font-size:30px">'''ERROR BARS'''</div> ==='''''Description:'''''=== '''''In Polar Charts, a series is represented by a closed curve that connects points in the pol...") |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="font-size:30px">'''ERROR BARS'''</div> | <div style="font-size:30px">'''ERROR BARS'''</div> | ||
==='''''Description:'''''=== | ==='''''Description:'''''=== | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''An error bar is a line through a point on a graph, parallel to one of the axes, which represents the uncertainty of the corresponding coordinate of the point.'''''<br> |
| − | ''' | + | '''Error Bars help to indicate estimated error or uncertainty to give a general sense of how exact a measurement is.'''''<br> |
| − | *''''' | + | *'''''Error Bars can be applied to graphs such as Scatter Plots, Dot Plots, Bar Charts or Line Graphs.'''''<br> |
| − | *''''' | + | *'''''This is done through the use of markers drawn over the original graph and its data points.'''''<br> |
| − | *''''' | + | *'''''Typically, Error bars are used to display either the standard deviation, standard error, confidence intervals or the minimum and maximum values in a ranged data-set.''''' |
| + | *'''''1st and 2nd column represents X and Y data-set, 3rd column represents error. | ||
==Example== | ==Example== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size:14px" | {| class="wikitable" style="font-size:14px" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | A|| '''B''' || '''C''' | + | | '''A'''|| '''B''' || '''C''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | '''X''' || '''Y''' || '''Error''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1.6 || 1.97 || 0.897 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2.51 || 3.1 || 0.732 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 3.55 || 2.79 || 0.633 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 3.83 || 3.96 || 0.6 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 5.47 || 4.4 || 0.633 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |5.77 || 5.72 || 0.732 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |6.89 || 7.2 || 0.897 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |7.76 || 7.65 || 1.128 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |8.78 || 8.34 || 1.425 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | '''ERRORBARS(A1: | + | '''ERRORBARS(A1:C10)'''<br><br/> |
[[File:errorbars.JPG]]<br><br/> | [[File:errorbars.JPG]]<br><br/> | ||
[[GRAPHING|'''''GRAPHING MAIN PAGE''''']] | [[GRAPHING|'''''GRAPHING MAIN PAGE''''']] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:18, 18 June 2020
ERROR BARS
Description:
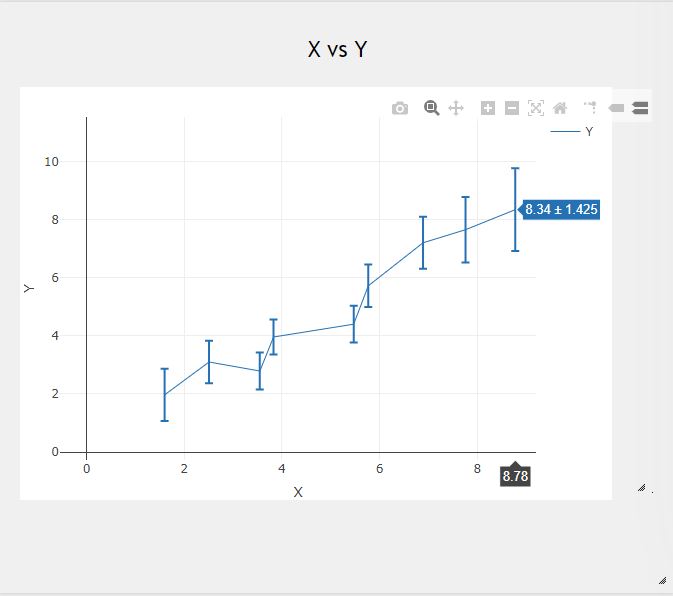
An error bar is a line through a point on a graph, parallel to one of the axes, which represents the uncertainty of the corresponding coordinate of the point.
Error Bars help to indicate estimated error or uncertainty to give a general sense of how exact a measurement is.
- Error Bars can be applied to graphs such as Scatter Plots, Dot Plots, Bar Charts or Line Graphs.
- This is done through the use of markers drawn over the original graph and its data points.
- Typically, Error bars are used to display either the standard deviation, standard error, confidence intervals or the minimum and maximum values in a ranged data-set.
- 1st and 2nd column represents X and Y data-set, 3rd column represents error.
Example
| A | B | C |
| X | Y | Error |
| 1.6 | 1.97 | 0.897 |
| 2.51 | 3.1 | 0.732 |
| 3.55 | 2.79 | 0.633 |
| 3.83 | 3.96 | 0.6 |
| 5.47 | 4.4 | 0.633 |
| 5.77 | 5.72 | 0.732 |
| 6.89 | 7.2 | 0.897 |
| 7.76 | 7.65 | 1.128 |
| 8.78 | 8.34 | 1.425 |
ERRORBARS(A1:C10)
GRAPHING MAIN PAGE