Difference between revisions of "Bartlett'sTest"
(→Result) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <div style="font-size:25px">'''BARTLETTSTEST(DataRange,ConfidenceLevel,NewTableFlag)'''</div | + | <div style="font-size:25px">'''BARTLETTSTEST(DataRange, ConfidenceLevel, NewTableFlag)'''</div> |
| − | *<math>DataRange</math> is the array of x values. | + | *'''<math>DataRange</math> is the array of x values. |
| − | *<math>ConfidenceLevel</math> is the value from 0 to 1. | + | *'''<math>ConfidenceLevel</math> is the value from 0 to 1. |
| − | *<math>NewTableFlag</math> is either TRUE or FALSE. TRUE for getting results in a new cube. FALSE will display results in the same cube. | + | *'''<math>NewTableFlag</math> is either TRUE or FALSE. TRUE for getting results in a new cube. FALSE will display results in the same cube.<br></br> |
| − | == | + | ==='''DESCRIPTION=== |
| − | * Bartlett's test is used to test if k samples are from populations with equal variances. | + | * '''Bartlett's test is used to test if k samples are from populations with equal variances. |
| − | * Bartlett's test is sensitive to departures from normality. | + | * '''Bartlett's test is sensitive to departures from normality. |
| − | * That is, if the samples come from non-normal distributions, then Bartlett's test may simply be testing for non-normality. | + | * '''That is, if the samples come from non-normal distributions, then Bartlett's test may simply be testing for non-normality. |
<math>B=\frac{df_WlnMS_W-\sum_{j}df_jln s_j^2}{1+\frac{1}{3(k-1)}(\sum_{j}\frac{1}{df_j}-\frac{1}{df_W})}</math> | <math>B=\frac{df_WlnMS_W-\sum_{j}df_jln s_j^2}{1+\frac{1}{3(k-1)}(\sum_{j}\frac{1}{df_j}-\frac{1}{df_W})}</math> | ||
| − | * B is the Bartlett's test static. | + | * '''B is the Bartlett's test static. |
| − | * <math>MS_W</math> is the pooled variance across all groups. | + | * '''<math>MS_W</math> is the pooled variance across all groups.<br></br> |
| − | == | + | ==='''RESULT=== |
| − | * If p-value is greater than BCritical value, reject the null hypothesis. | + | * '''If p-value is greater than BCritical value, reject the null hypothesis. |
| − | * Else retain null hypothesis. | + | * '''Else, retain null hypothesis.<br></br> |
| − | == | + | ==='''EXAMPLE=== |
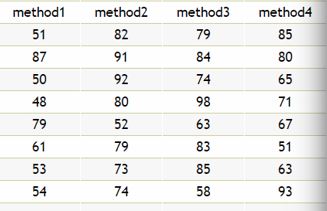
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+Spreadsheet | |+Spreadsheet | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
|54 || 74 || 58 || 93 | |54 || 74 || 58 || 93 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | =BARTLETTSTEST([A1:A8,B1:B8,C1:C8,D1:D8],0.05,true) | + | ='''BARTLETTSTEST([A1:A8, B1:B8, C1:C8, D1:D8], 0.05, true)<br></br> |
| + | |||
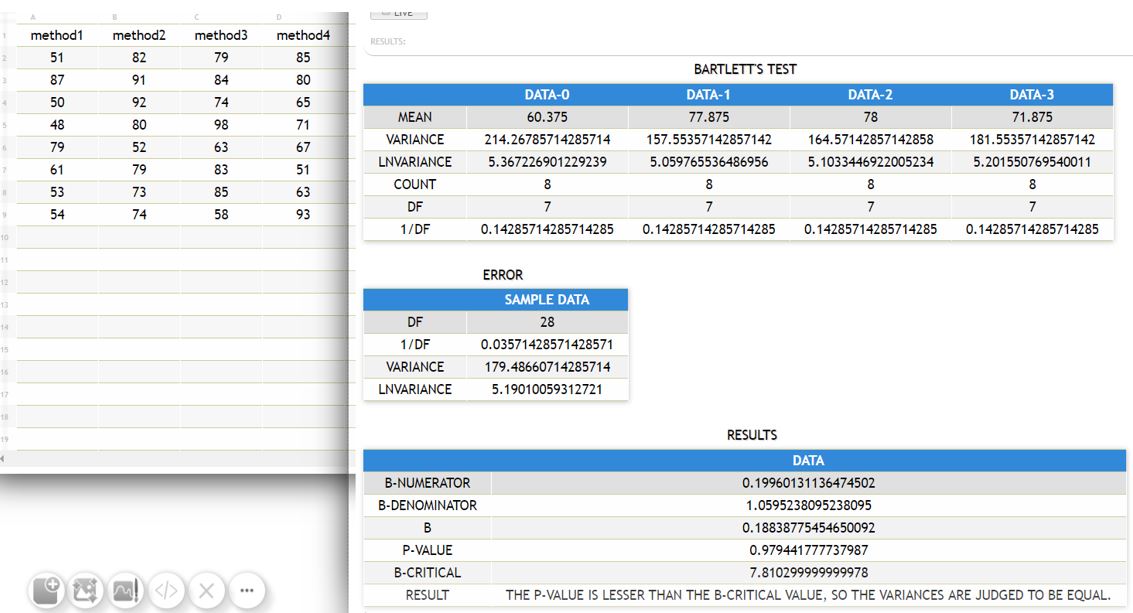
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+BARTLETT'S TEST | |+BARTLETT'S TEST | ||
| Line 90: | Line 91: | ||
|P-VALUE || 0.979441777737987 | |P-VALUE || 0.979441777737987 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |B-CRITICAL || 7. | + | |B-CRITICAL || 7.814684159999997 |
|- | |- | ||
|RESULT || THE P-VALUE IS LESSER THAN THE B-CRITICAL VALUE, SO THE VARIANCES ARE JUDGED TO BE EQUAL. | |RESULT || THE P-VALUE IS LESSER THAN THE B-CRITICAL VALUE, SO THE VARIANCES ARE JUDGED TO BE EQUAL. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | <br></br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Comparison with other software=== | ||
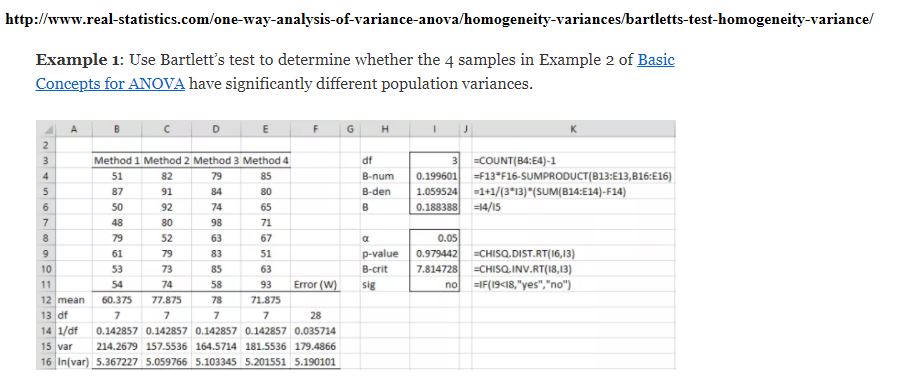
| + | '''Bartlett's test to determine whether the 4 samples have significantly different population variances.<br><br> | ||
| + | [[File:bart1.JPG]]<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''SOLUTION'''<br> | ||
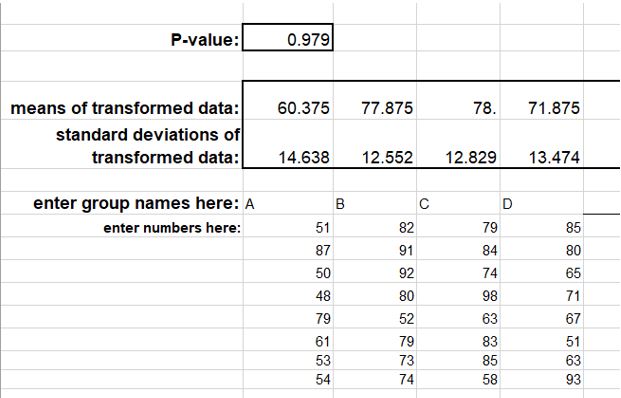
| + | '''In z3:'''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:bartz.JPG]]<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
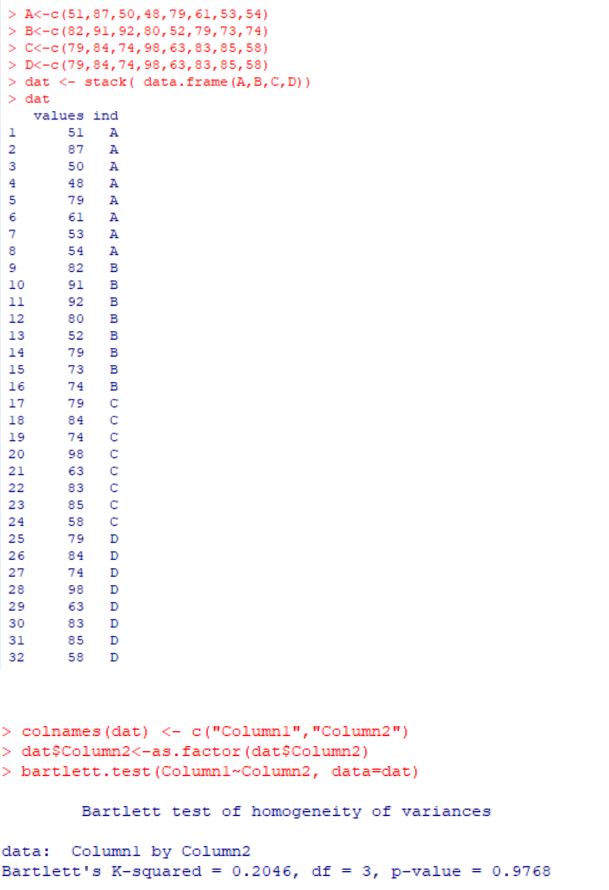
| + | '''In R:'''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:bartr.JPG]]<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''In Online Software:'''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:bartos.JPG]]<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''In Online Software:'''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:bartos2.JPG]]<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * z3 and the online software give the same P-value i.e 0.979. | ||
| + | * R has a P-value of 0.9768. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:31, 19 August 2020
BARTLETTSTEST(DataRange, ConfidenceLevel, NewTableFlag)
- is the array of x values.
- is the value from 0 to 1.
- is either TRUE or FALSE. TRUE for getting results in a new cube. FALSE will display results in the same cube.
DESCRIPTION
- Bartlett's test is used to test if k samples are from populations with equal variances.
- Bartlett's test is sensitive to departures from normality.
- That is, if the samples come from non-normal distributions, then Bartlett's test may simply be testing for non-normality.
- B is the Bartlett's test static.
- is the pooled variance across all groups.
RESULT
- If p-value is greater than BCritical value, reject the null hypothesis.
- Else, retain null hypothesis.
EXAMPLE
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 51 | 82 | 79 | 85 |
| 2 | 87 | 91 | 84 | 80 |
| 3 | 50 | 92 | 74 | 65 |
| 4 | 48 | 80 | 98 | 71 |
| 5 | 79 | 52 | 63 | 67 |
| 6 | 61 | 79 | 83 | 51 |
| 7 | 53 | 73 | 85 | 63 |
| 8 | 54 | 74 | 58 | 93 |
=BARTLETTSTEST([A1:A8, B1:B8, C1:C8, D1:D8], 0.05, true)
| DATA-0 | DATA-1 | DATA-2 | DATA-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN | 60.375 | 77.875 | 78 | 71.875 |
| VARIANCE | 214.26785714285714 | 157.55357142857142 | 164.57142857142858 | 181.55357142857142 |
| LNVARIANCE | 5.367226901229239 | 5.059765536486956 | 5.1033446922005234 | 5.201550769540011 |
| COUNT | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| DF | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 1/DF | 0.14285714285714285 | 0.14285714285714285 | 0.14285714285714285 | 0.14285714285714285 |
| SAMPLE DATA | |
|---|---|
| DF | 28 |
| 1/DF | 0.03571428571428571 |
| VARIANCE | 179.48660714285714 |
| LNVARIANCE | 5.19010059312721 |
| DATA | |
|---|---|
| B-NUMERATOR | 0.19960131136474502 |
| B-DENOMINATOR | 1.0595238095238095 |
| B | 0.18838775454650092 |
| P-VALUE | 0.979441777737987 |
| B-CRITICAL | 7.814684159999997 |
| RESULT | THE P-VALUE IS LESSER THAN THE B-CRITICAL VALUE, SO THE VARIANCES ARE JUDGED TO BE EQUAL. |
Comparison with other software
Bartlett's test to determine whether the 4 samples have significantly different population variances.
- z3 and the online software give the same P-value i.e 0.979.
- R has a P-value of 0.9768.
 is the array of x values.
is the array of x values. is the value from 0 to 1.
is the value from 0 to 1. is either TRUE or FALSE. TRUE for getting results in a new cube. FALSE will display results in the same cube.
is either TRUE or FALSE. TRUE for getting results in a new cube. FALSE will display results in the same cube.
 is the pooled variance across all groups.
is the pooled variance across all groups.