Coding
Thinking in z^3
This is a quick introduction to the z^3 language (pronounced as "zcubes language").
z^3 is an easy to write, natural to read, language powered by high performance computing. Learn z^3 Language in detail by clicking this link.
An introduction to z^3 Code Mode in ZCubes is detailed below.
Code Mode in ZCubes
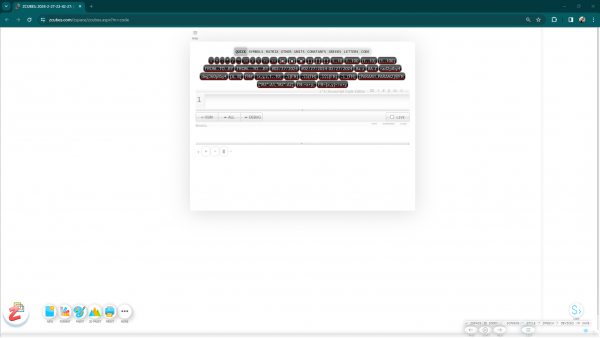
To test the ZCubes platform in code mode,Visit https://code.zcubes.com
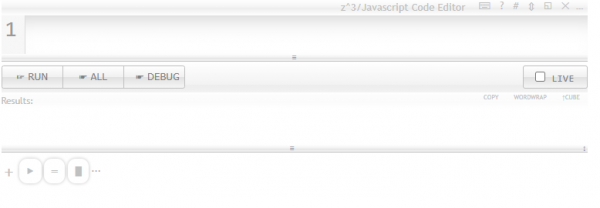
Enter code in the code editor and press run to execute.
Running z^3 code in ZCubes Browser (or) ZAP Desktop Interface
If you open a Code Command Editor in ZCubes platform, clicking on the keyboard icon on top right (⌨) shows (and toggles) the Keyboard Helper for z^3 language as given below. In ZCubes Code Mode, this panel is automatically shown. Clicking on ? shows helpful information on editor key commands. Clicking on # shows a list of functions or member functions that can be used in the context. ⇕ and ◱ allow resizing the code editor window in different ways. Pressing Run runs the code. Ctrl+Run will evaluate current selection in the editor. Shift+Run will evaluate current active line in the code editor. If the Browser Debugger is switched on, and if Debug button is pressed, the code inside can be debugged in the browser debugger itself.
ZCubes Code Mode Control Panel
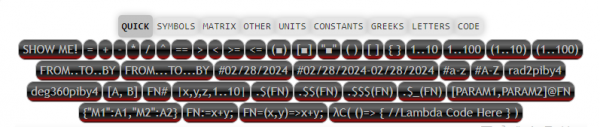
The responsive Keyboard Helper Panel tabs can be used to select code templates, symbols, units, etc. to be inserted into the coding area.
Intellisense
Listing of functions can be obtained by Ctrl+Space in the editor. Member functions show up on appropriate parts of the code with the same Ctrl+Space key combination.
Quick Panel
Note that the Show Me button shows the coding page to provide a gentle introduction to coding using z^3 language.
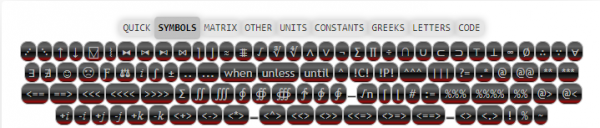
Symbols Panel
Symbols panel gives quick access to operators in z^3, and a wide variety of useful symbols that are useful in programming with z^3.
Matrix Panel
Other Panel
Units Panel
Pick Unit type and get access to Units supported by z^3 to be used in programs and conversions.
Constants Panel
Pick to insert constants with units supported by z^3 into the code editor to be used in programs and conversions.
Greeks Panel
Pick upper and lower case Greek letters to code with.
Letters and Numbers Panel
Code Template Panel
Insert code templates for quick insertion into the Code Editor.
Several of the key features are listed below, with examples. Code segments below can be copied and pasted to the ZCubes code editor to execute.
Series Comprehension
1..100..2 1...1000000...2 ..40 rad2piby30 deg360by15 #a-z [MONTHS,DAYS, PLANETS] // #1/20/2024-1/20/2025
@ & Combinatorial Arguments
- Array of Functions apply to Array of Data (@)
- Combinatorial Arguments
- Avoids Loops
- Combinatorial Arguments
- Functions apply Function (@)
- Easy Function Definition
1..10@SIN; [3..10,5..10]@CHIDIST; 1..10@[SIN,COS,"x^2"];
Units & Constants
- 4m, 40ly, 45(m/s)
- %g, %c, %avo
- Seamless in Functions
%g; %avo; %plan; 45(m/s); 34m<*>45cm; π; /* energy mass equation */ units.on; // triggers array-based units calc Energy:=mass*%c^2; Energy(1kg) 45°<>㎭; 45℃<>℉; units.on; AreaOfCircle:=π*r^2; AreaOfCircle((1..10)<>m)
Arrays, Matrices, Collections
- |x|
- Creation
- a|x^y| b
- Array Functions
- Array Member Functions
- Array Sensitive Functions
- Arrayfy Operator
- Related: Queues, Stacks, Graphs, Sets, Maps, etc.
|5|; |3,4,4,1..10|; 1..10|x^2|3; 1..10|x+y^2|11..20; SIN(1..10); 1..10.chunks(5); 1..10.parts(5); 1..10.pieces(3) v:=u+a*t; v ⩨; v(0..5,3..5,6..10); [0..5,3..5,6..10]@v SIN(deg360by20); a1=1..10; a1.across(a1,SUM); (1..100@SIN).graph()
Portability & Extensibility
- Multi Platform
- Windows, Mac, Linux, Browser
- Multi-Modal
- Browser, Desktop, CLIServer, Web-Server, IoT
- Compatibility
- npmjs & js libraries
- Native Interfaces
- Browser Integration
- Integrated Functionality
a=$(".zcube").length;
addsq:=a^2+b^2;
Advanced Types
- Big Numbers
- High Accuracy Floats
- Fractions
- Complex Numbers
- Array Based Computation
- units.on;
- Render (2D and 3D)
- Programming Media
- Symbolic Algebra
(100n)! ;
(1.3%%5)^2;
SIN(2+34i);
(3+4i)!;
SIN((1..4)+(3..4)<>i);
PI(100);
units.on;
(1/3d50)*3;
// circle around polygon points
pts=MAKEPOLYGONPOINTS(50,200)
.concat(MAKEPOLYGONPOINTS(50,100))
RENDER(
[
["type","cx","cy","r","stroke","stroke-width","fill","count"],
["circle",i=>300+pts[i][0],i=>300+pts[i][1],100,"black",1,i=>"transparent",pts.length]
]
)
""
// circle around polygon points
noofpoints=50;
pts=MAKEPOLYGONPOINTS(noofpoints,[100,100],[300,300],-90)
start=pts[0];
circlesat=
pts
.map(
p=>[p[0],p[1],SQRT(POWER(p[0]-start[0],2)+POWER(p[1]-start[1],2))]
)
RENDER(
[
["type","cx","cy","r","stroke","stroke-width","count"],
["circle",circlesat.column(0),circlesat.column(1),circlesat.column(2), i=>d3.interpolateInferno(i/circlesat.length) ,1,circlesat.length]
]
)
""
Other Modes
- Browser
- CLI
- Desktop
- Server
- Web Server
- Over 100 In Production
- Examples
Scaling Up
z^3 can be used in a variety of platforms, and for any scale of programs. The versatility of the language makes it very useful to solve intricate problems, and we hope the language may trigger everyone to think of programming logic as a natural part of intellectual activity.
Simple. Powerful. Versatile.